- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
Key materials and technical status of AEM water electrolysis hydrogen production system
2025-01-06
AEM is the abbreviation of solid polymer anion exchange membrane water electrolysis. AEM water electrolysis technology has huge room for cost reduction. It is one of the most cutting-edge water electrolysis technologies and one of the preferred technologies for large-scale application of green hydrogen in the future.
Today, let's take a look at the key materials and technical development of AEM water electrolysis hydrogen production system.
1. Basic working principle
AEM water electrolysis technology combines the advantages of alkaline water electrolysis technology and PEM water electrolysis technology. Compared with alkaline water electrolysis technology, AEM technology has a faster response speed and higher current density; and compared with PEM water electrolysis technology, AEM technology has a lower manufacturing cost.
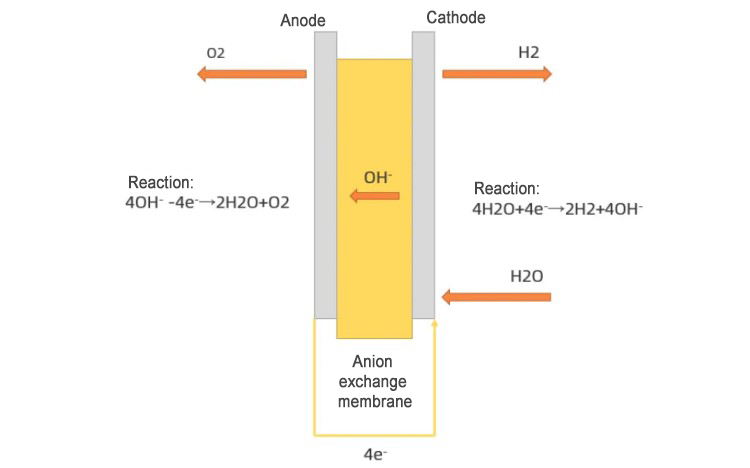
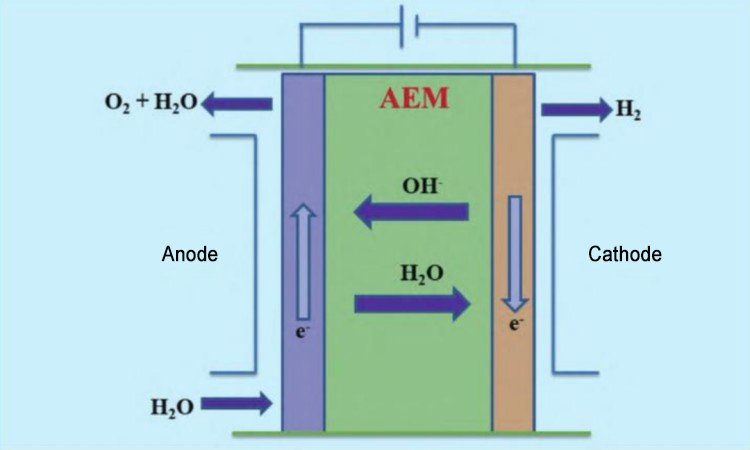
Schematic diagram of AEM water electrolysis equipment
As shown in the figure, when the equipment is running, the raw water enters from the cathode side of the AEM equipment. Water molecules participate in the reduction reaction at the cathode and obtain electrons to generate hydroxide ions and hydrogen. After the hydroxide ions reach the anode through the polymer anion exchange membrane, they participate in the oxidation reaction and lose electrons to generate water and oxygen. Depending on the design of the equipment, a certain amount of KOH solution or NaHCO3 solution is sometimes added to the raw water as an auxiliary electrolyte, which helps to improve the working efficiency of the AEM electrolysis equipment.
The AEM electrolytic cell is the basic unit of the AEM electrolysis system. Multiple AEM electrolytic cells together form an AEM electrolysis module. A large number of AEM electrolytic modules and multiple auxiliary systems together constitute the AEM water electrolysis system. Among them, the auxiliary system includes hydrogen treatment and drying system, water tank, water treatment purification system and AC-DC converter, etc.
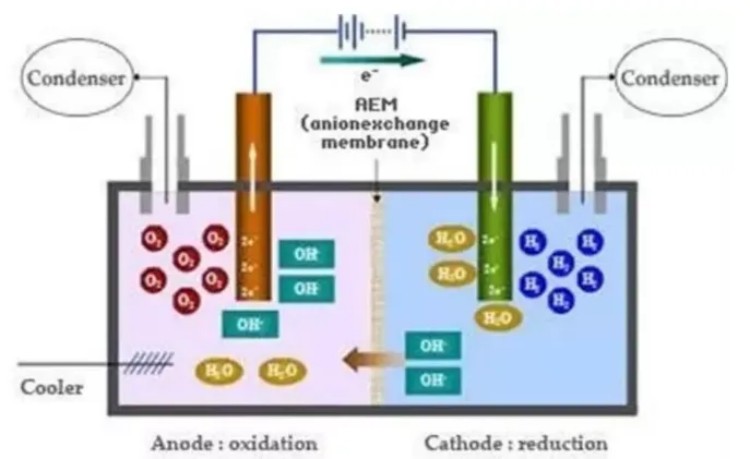
AEM electrolytic cell: cathode material, anode material and anion exchange membrane are the core components of the AEM electrolytic cell, which directly affect the working efficiency and equipment life of the AEM electrolytic cell.
2. Key raw materials
1. Anion exchange membrane
The anion exchange membrane is the most important part of the AEM electrolytic cell, which directly determines the working efficiency and operating life of the AEM electrolytic equipment. The function of the anion exchange membrane is to conduct hydroxide ions from the cathode to the anode. Therefore, the material constituting the anion exchange membrane needs to have high anion conductivity and extremely low electron conductivity.
Since high alkalinity will appear in local areas in AEM electrolysis equipment, under ideal conditions, anion exchange membranes need to have excellent chemical and mechanical stability. At the same time, in order to isolate the cathode and anode and prevent hydrogen and oxygen from contacting each other and causing explosions, anion exchange membranes must have extremely low gas permeability.
At present, polymers are usually used as the main material of anion exchange membranes. Since AEM water electrolysis technology is still in the research and development stage, the most suitable material has not been found at this stage. Aromatic polymers are used more in research and development.
There are still many problems in the selection of materials:
1. Aromatic polymers will be slowly degraded when operating in an alkaline environment for a long time, especially when a dilute KOH solution is added as an auxiliary electrolyte, affecting the stability and system life of the AEM water electrolysis equipment;
2. Since the conductivity of hydroxide ions in anion exchange membranes is much lower than that in proton exchange membranes, in order to maintain the working efficiency of AEM electrolysis cells, research and development institutions tend to make thinner anion exchange membranes to reduce the resistance to hydroxide ion conduction, but this will also reduce the mechanical stability of the anion exchange membrane, making it prone to voids.
2. Cathode materials and anode materials
The main function of cathode materials and anode materials is to catalyze the decomposition reaction of water and output the generated hydrogen and oxygen in time. Therefore, cathode and anode materials must have strong catalytic activity and porosity. In order for the electrode reaction to proceed smoothly, cathode and anode materials must have high anion conductivity and electron conductivity.
At present, the most commonly used cathode materials are mainly nickel, and the anode materials are mainly nickel-iron alloys. Iron and nickel not only have strong catalytic activity for the decomposition of water, but also have wide sources and low costs. Since AEM does not need to operate in a highly corrosive environment, precious metal catalysts such as ruthenium and titanium do not need to be added to the anode and cathode materials. This greatly reduces the manufacturing cost of AEM equipment.
The anion exchange membrane currently developed still cannot take into account both work efficiency and equipment life. Therefore, research on AEM mainly focuses on the development of suitable and efficient polymer anion exchange membranes. Secondly, in the laboratory research and development stage, a small amount of precious metals will still be added to the electrode materials. Therefore, the development of low-cost, efficient non-precious metal catalysts is also one of the focuses of AEM research.